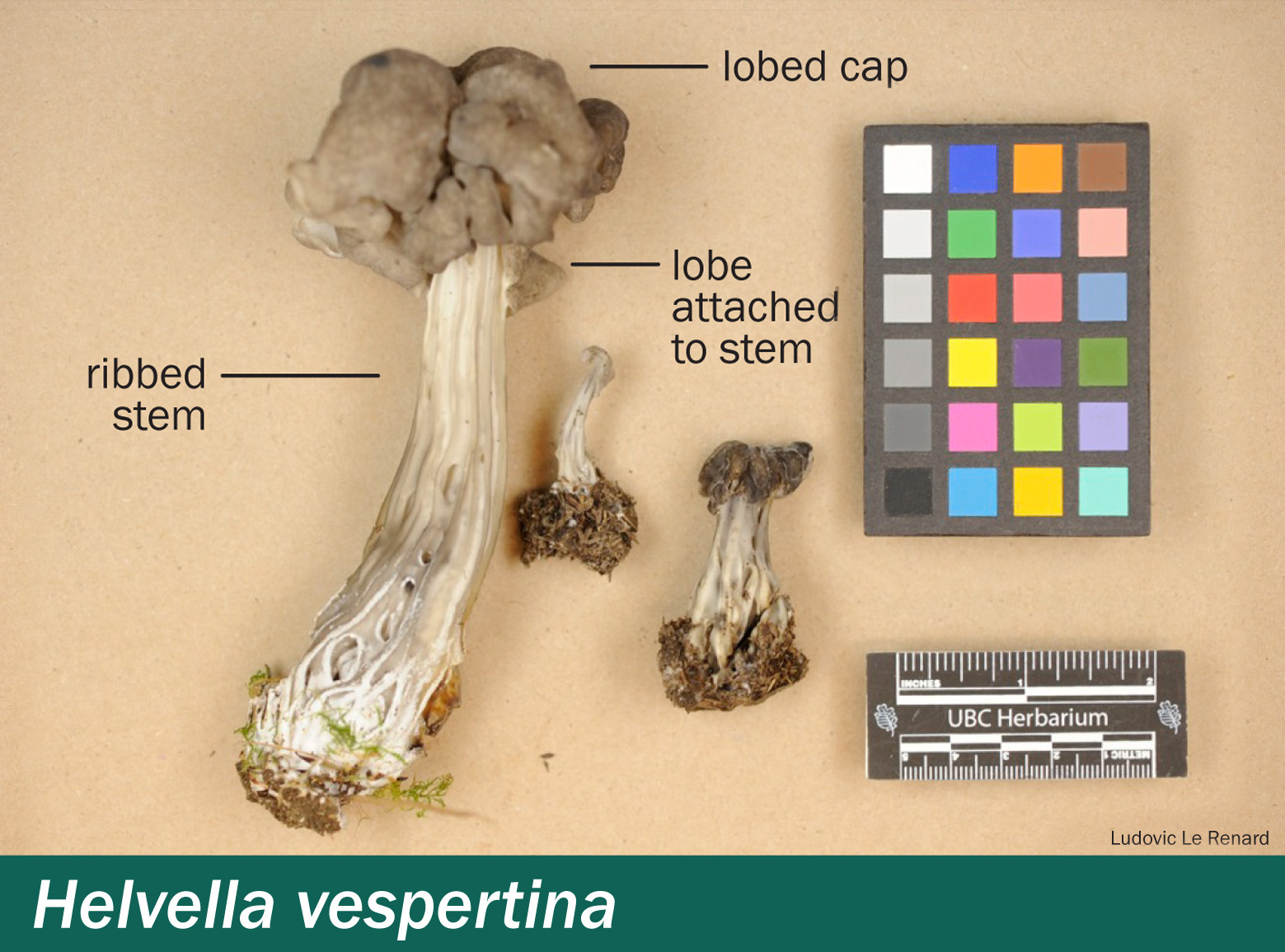
Helvella vespertina — Western elfin saddle
Odour: None.
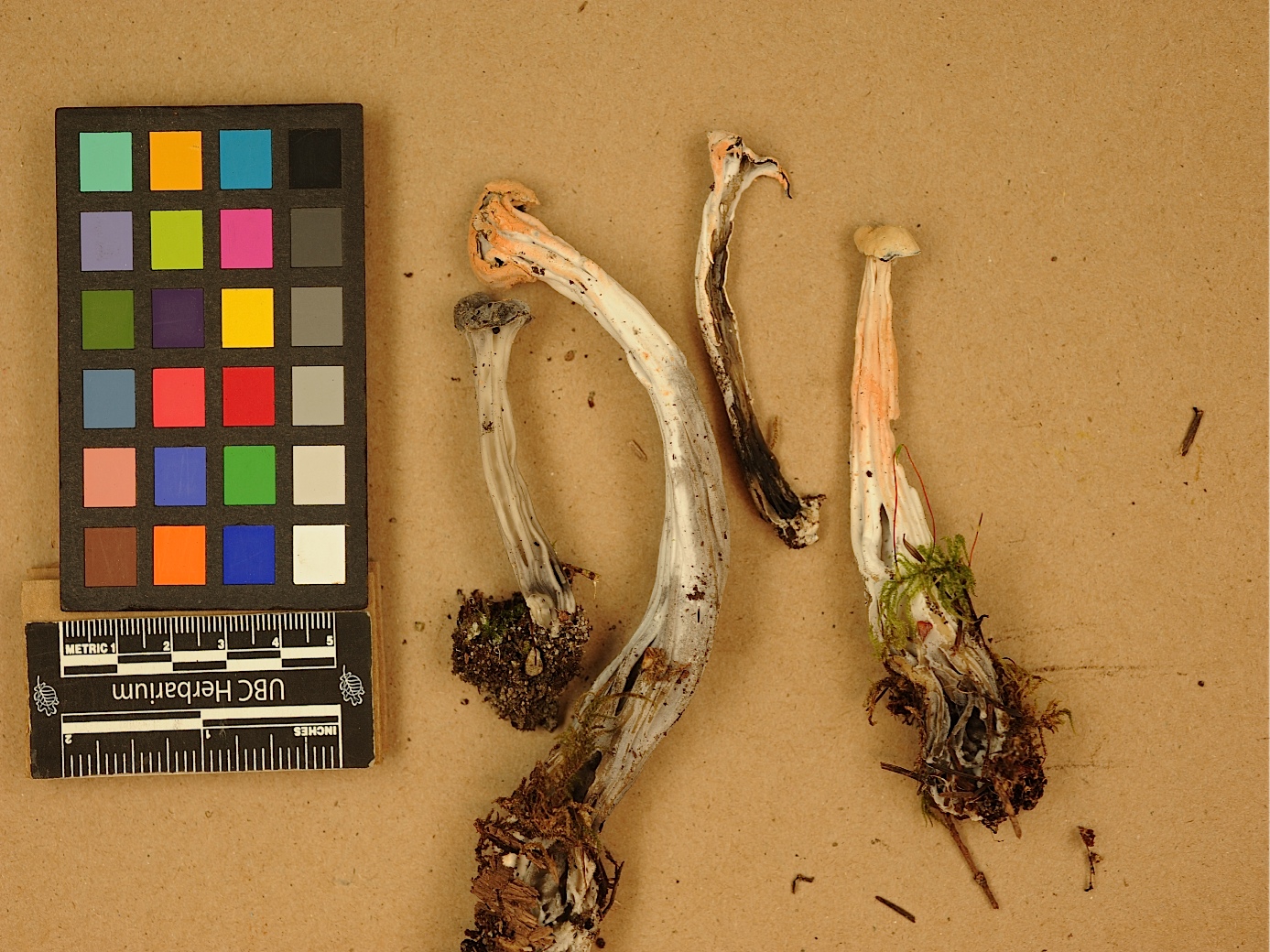
Cap: 2.5–5(–12) cm in diameter, 2.5–5.5(–15) cm high, with three lobes. These lobes become convoluted and brain-like with age, often with one lobe hanging down. The lobes' surfaces are smooth and they are often attached to the stem in one or more places. The colour of the outer surface of the lobes may be light or dark grey, or brownish. The inner lobe surface is light to dark grey.
Stem: Up to 25 cm long and up to 20 mm wide. The stem is cylindrical, with sharp-edged lengthwise ribs and holes. Cross sections show that the stem has one or more hollow chambers. The colour is white, often becoming grey in age, and sometimes ochre-yellow in lower part.
Ring or veil: None.
Cup: None.
Spores: 16–21 x 10–12.5 µm, smooth, white.
Habitat: On the ground, growing with coniferous trees, such as Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), and pines (Pinus spp.); ectomycorrhizal.
Geographic distribution: In western North America from southern California on the coast and in the mountains, northwards into BC, Rocky Mountains4. Occasionally, it has been collected from eastern North America4,5. As the species was named and described in 20133, the full range of the species remains to be discovered.
Helvella elastica has a saddle-shaped cap and a slender, smooth stem. Gyromitra infula with its three lobes like a pirate’s hat, looks like a Helvella, but always grows on conifer wood. Gyromitra infula has a brown cap, and a purplish brown stem. Other Gyromitra species have brown, convoluted brain-like caps. Gyromitra species contain the unstable chemical gyromitrin that is hydrolyzed to highly toxic monomethylhydrazine.
The western elfin saddle is often covered and parasitized by Hypomyces cervinigenus, a white mold that turns pale orange-pink with age. Another parasite, Clitocybe sclerotoidea forms its fruitbodies out of colonized misshapen and aborted western elfin saddle fruitbodies.
Treatment: Contact your regional Poison Control Centre if you or someone you know is ill after eating elfin saddles. Poison centres provide free, expert medical advice 24 hours a day, seven days a week. If possible, save the mushrooms or some of the leftover food containing the mushrooms to help confirm identification.
Poison Control:
British Columbia: 604-682-5050 or 1-800-567-8911.
United States (WA, OR, ID): 1-800-222-1222.